Under the Canadian constitution, the power to establish criminal law and rules of investigation is vested in the federal Parliament. The provinces share responsibility for law enforcement (although provincial policing in many jurisdictions is contracted to the federal Royal Canadian Mounted Police), and while the power to prosecute criminal offences is assigned to the federal government, responsibility for prosecutions is delegated to the provinces for most types of criminal offences. Laws and sentencing guidelines are uniform throughout the country, but provinces vary in their level of enforcement.
Statistics Canada data
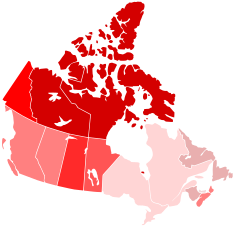
There were 2,452,787 crimes reported in 2006; 48% were property-related crimes and 12.6% were violent crimes. At a rate of 7,518 reported incidents per 100,000 people, the crime rate in 2006, the latest year for which there is statistics, was the lowest crime rate in twenty-five years. The crime rate has been in general decline since 1991.
The province with the lowest crime rate in 2006 for the third straight year was Ontario with 5,689 per 100,000, followed by Quebec with 5,909 per 100,000. The province with the highest crime rate for the 9th straight year was Saskatchewan with 13,711 per 100,000. Regina is the city with the highest crime rate followed by its provincial counterpart Saskatoon. Quebec City, Trois-Rivières, and Saguenay have the lowest crime rates of any city and are all located in Quebec. Winnipeg has had the highest violent crime rate since 2009 and still held it in 2012. For years native Canadian women have been victims of sexual assault and murder disproportionately often and there have been complaints that the police paid insufficient attention to the problem. The three northern territories have higher per capita crime rates than any province. As evidenced by the crime map above right, Saskatchewan has a higher crime rate than the other Canadian provinces, but lower than the territories.
The number of murders dropped to 594 in 2007, 12 fewer than the previous year. One-third of the 2007 murders were stabbings and another third were by firearm. In 2007, there were 190 stabbings and 188 shootings. Handguns were used in two-thirds of all firearm murders. Seventy-four youths were accused of murder, down 11 from the previous year. About eighty-four percent of murders were done by someone known to the victim. Male victims of homicide were most likely to be killed by an acquaintance, someone known to them through a criminal relationship, or a stranger. Female victims of homicide were most frequently killed by a current or former intimate partner, or another family member. The province with the highest crime rate was Manitoba while the lowest crime rates occurred in Prince Edward Island and Newfoundland and Labrador.
Police reported criminal violence is thought to be an undercount of actual violence rates. Thus, approximately every five years, Statistics Canada conducts a survey of victimization in Canada. The last General Social Survey conducted was in 2004, where 24,000 people were contacted by telephone: 106 reported incidents of violence per 1,000 polled, which is slightly lower than in 1999 when it was 111 per 1,000 polled.
Crime by region
Murder Capitals since 1981
Winnipeg has been the "Murder Capital" of Canada 16 times since homicide rates have been available in 1981, far exceeding any other city.
Violent crime severity index by CMA
Winnipeg is the most violent city in Canada.
Crime statistics by province and territory
Crime statistics vary considerably through different parts of Canada. In general, the eastern provinces have the lowest violent crime rates while the western provinces have higher rates and the territories higher still. Of the provinces, Manitoba and Saskatchewan have the highest violent crime rates. The chart below also shows that Saskatchewan has the highest assault rate, and that Manitoba has the highest sexual assault rate, robbery rate and homicide rate of any Canadian province.
2012 crime statistics for the provinces and territories are given below, as reported by Statistics Canada.
Guns
Gun ownership rates in Canada are approximately the average for the developed countries (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)), and far below those of the United States. Approximately 15.5% of Canadian households owned firearms in 2004-2005, including 2.9% that owned handguns; these rates are similar to the averages for the OECD (14.2% and 3.4%, respectively), whereas nearly three times as many American households (42.8%) own firearms, and nearly six times as many (17.6%) own handguns. Typically, the firearm ownership rate in rural areas is much higher than in urban areas, and higher in western Canada than in the east. The majority of Canadian firearms include rifles, shotguns, and pistols. Firearms are readily available to licensed Canadian citizens, with restrictions on handguns. Fully automatic firearms are an exception and are generally prohibited from private ownership.
It is effectively illegal to carry concealed handguns in Canada. There is a permit that allows people to carry if they can prove they need to protect their lives under specific circumstances, but the permit is very rarely issued to civilians. The topic of Authorization To Carry (ATC) permits has been a long standing topic of issue among legal firearm owners in Canada. The Canadian Association for Self Defense and the National Firearms Association are lobbying for an amendment to the Canadian Firearms Act to enable law abiding citizens to more easily attain ATC permits.
Police
In 2005, there were 61,050 police officers in Canada which equates to one police officer per 528.6 persons, but with significant regional variations. Newfoundland and Labrador and Prince Edward Island have the fewest police per capita with 664.9 and 648.4 persons per police officer, respectively. Conversely, the highest ratio of police to population is found in Canada's northern territories; Nunavut has 247.9 persons per police officer, the Northwest Territories has 248.5 persons per officer and the Yukon has 258.2 persons for each police officer.
That is a substantially lower rate than most developed countries with only Japan and Sweden having so few police officers. The United States has one officer per 411.5 persons, and Germany 344.8.
Canada's national police force is the Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP) which is the main police force in Canada's north, and in rural areas except in Quebec, Ontario, and Newfoundland. Those three provinces have their own provincial police forces, although the RCMP still operate throughout rural Newfoundland and also provide specific federal policing services in Ontario and Quebec. Many cities and districts have their own municipal police forces, while others have contracts with the provincial police or RCMP to police their communities.
Report rates of crimes
A publication posted on Statistics Canada reported that in 2009, only a small portion of crimes that happen are reported to the police (31% of all crimes), and this figure has been lowering from 1999 (37%) and 2004 (34%). Only 54% of break and enters, 43% of robberies, and 34% of assaults are reported to the police. The most common reason for not reporting a crime was the victim thought it was not important enough (68%). Other common reasons include; they think the police cannot do anything about it (59%), or they dealt with it another way (42%). Keep in mind people can give multiple reasons, thus why the percentages equal well over 100%.
Punishment
There is controversy among criminologists over whether harsh sentences are a cause or a reflection of higher crime rates. Compared to the United States, the length of prison sentences in Canada have been shorter throughout the twentieth century, even during periods when the two countries' crime rates were comparable.
Canada has relatively short sentences for many crimes and most convicts receive parole after serving two thirds of their sentence. Canada abolished the death penalty for murder in 1976, Sentences for drug-related crimes are shorter, and less harsh, than sentences in the United States, Australia, and other western nations.
In 2001, Canada had about 32,000 people in prison or about 0.13% of the total population. Globally, the United States was the country with the highest percentage of inmate population (about 0.7% of the total population). The European average is of 0.2% of the total population, with France and Germany having lower rates than Canada, but with the United Kingdom, Spain and most of Eastern Europe having higher ones.
Although Aboriginal persons make up 3.6% of Canada's population, they account for more than 20% of Canada's prison population.
Comparisons
Comparing crime rates between countries is difficult due to the differences in jurisprudence, reporting and crime classifications. National crime statistics are in reality statistics of only selected crime types. Data is collected through various surveying methods that have previously ranged between 15% and 100% coverage of the data. A 2001 Statistics Canada study concluded that comparisons with the U.S. on homicide rates were the most reliable. Comparison of rates for six lesser incident crimes was considered possible but subject to more difficulty of interpretation. For example, types of assaults receive different classifications and laws in Canada and the US, making comparisons more difficult than homicides. At the time, the U.S. crime of aggravated assault could be compared to the sum of three Canadian crimes (aggravated assault, assault with a weapon, and attempted murder). This comparison had a predicted bias that would inflate the Canadian numbers by only 0.1%. The study also concluded that directly comparing the two countries' reported total crime rate (i.e. total selected crimes) was "inappropriate" since the totals include the problem data sets as well as the usable sets. For reasons like these, homicides have been favored in international studies looking for predictors of crime rates (predictors like economic inequality).
United States
Much study has been done of the comparative experience and policies of Canada with its southern neighbour the United States, and this is a topic of intense discussion within Canada.
Historically, the violent crime rate in Canada is far lower than that of the U.S. and this continues to be the case. For example, in 2000 the United States' rate for robberies was 65 percent higher, its rate for aggravated assault was more than double, and its murder rate was triple that of Canada. However, the rate of some property crime types is lower in the U.S. than in Canada. For example, in 2006, the rates of vehicle theft were 22% higher in Canada than in the US.
Furthermore, in recent years, the gap in violent crime rates between the United States and Canada has narrowed due to a precipitous drop in the violent crime rate in the U.S. For example, while the aggravated assault rate declined for most of the 1990s in the U.S. and was 324 per 100,000 in 2000, the aggravated assault rate in Canada remained relatively steady throughout and was 143 per 100,000 in 2000. In other areas, the U.S. had a faster decline. For instance, whereas the murder rate in Canada declined by 36% between 1991 and 2004, the U.S. murder rate declined by 44%.
The homicide rate in Canada peaked in 1975 at 3.03 per 100,000 and has dropped since then; it reached lower peaks in 1985 (2.72) and 1991 (2.69). It reached a post-1970 low of 1.73 in 2003. The average murder rate between 1970 and 1976 was 2.52, between 1977 and 1983 it was 2.67, between 1984 and 1990 it was 2.41, between 1991 and 1997 it was 2.23 and between 1998 to 2004 it was 1.82. The attempted homicide rate has fallen at a faster rate than the homicide rate.
By comparison, the homicide rate in the U.S. reached 10.1 per 100,000 in 1974, peaked in 1980 at 10.7 and reached a lower peak in 1991 (10.5). The average murder rate between 1970 and 1976 was 9.4, between 1977 and 1983 it was 9.6, between 1984 and 1990 it was 9, between 1991 and 1997 it was 9.2 and between 1998 and 2004 it was 6.3. In 2004, the murder rate in the U.S. dipped below 6 per 100,000, for the first time since 1966, and as of 2010 stood at 4.8 per 100,000
In more recent years, the USA as a country still typically has higher violent crimes rates. In 2012, the homicide rate in the USA was 4.7 per 100,000 residents, Canada's was 3 times lower at 1.6, however one should note the chances of being murdered at random are extremely low in both countries. In Canada, only 15% of murders are committed by strangers, in the USA this number is very similar at 14%, meaning in 50 years your chance of being murdered at random is 0.000128% in Canada, in the USA it is 0.000329% (of course these numbers would vary by neighborhoods within each country). Certain methods of homicide are used more frequently in each country; in Canada (0.59), stabbing homicides occur 51.3% more often than in the USA (0.39), however firearm homicides occur 440% more in the USA (2.7) than in Canada (0.5). In the USA, you are 3 times more likely to die being shot (17.4%) then being stabbed (5.3%).
Beyond homicides, the USA (112.9) has a higher robbery rate - 42.2% higher than Canada (79.4). Other violent crimes such as physical assaults or sexual assaults are not very comparable between the countries because of different definitions of the crimes. The disparity in property crime is not as large, however it still exists. The burglary/break-in rate in the USA (670.2) is 33.1% higher than in Canada (503.7), the theft rate in the USA (1959.3) is 33.4% higher than in Canada (1468.4), and the auto-theft rate in the USA (229.7) is slightly higher than the rate in Canada (223.5).
See also
- Gangs in Canada
- Political scandals in Canada
- Computer crime in Canada
- Terrorism in Canada
References
Further reading
External links
- Correctional Service Canada (commonly called Corrections Canada) administers federal prisons and parole boards.
- Crime comparisons between Canada and the United States
- Black markets in Canada
