Life expectancy is a statistical measure of how long a person or organism may live, based on the year of their birth, their current age and other demographic factors including gender. At a given age, life expectancy is the average number of years that is likely to be lived by a group of individuals (of age x) exposed to the same mortality conditions until they die. The most commonly used measure of life expectancy is life expectancy at age zero, that is, at birth (LEB), which can be defined in two ways: while cohort LEB is the mean length of life of an actual birth cohort (all individuals born a given year) and can be computed only for cohorts that were born many decades ago, so that all their members died, period LEB is the mean length of life of a hypothetical cohort assumed to be exposed since birth until death of all their members to the mortality rates observed at a given year.
National LEB figures reported by statistical national agencies and international organizations are indeed estimates of period LEB. In the Bronze and Iron Age LEB was 26 years; the 2010 world LEB was 67.2. For recent years in Swaziland LEB is about 49 years while in Japan is about 83 years. The combination of high infant mortality and deaths in young adulthood from accidents, epidemics, plagues, wars, and childbirth, particularly before modern medicine was widely available, significantly lowers LEB. But for those who survive early hazards, a life expectancy of sixty or seventy would not be uncommon. For example, a society with a LEB of 40 may have few people dying at age 40: most will die before 30 years of age or very few after 55. In countries with high infant mortality rates, LEB is highly sensitive to the rate of death in the first few years of life. Because of this sensitivity to infant mortality, LEB can be subjected to gross misinterpretation, leading one to believe that a population with a low LEB will necessarily have a small proportion of older people. For example, in a hypothetical stationary population in which half the population dies before the age of five, but everybody else dies at exactly 70 years old, LEB will be about 36 years, while about 25% of the population will be between the ages of 50 and 70. Another measure, such as life expectancy at age 5 (e5), can be used to exclude the effect of infant mortality to provide a simple measure of overall mortality rates other than in early childhoodâ€"in the hypothetical population above, life expectancy at age 5 would be another 65 years. Aggregate population measures, such as the proportion of the population in various age groups, should also be used alongside individual-based measures like formal life expectancy when analyzing population structure and dynamics.
Mathematically, life expectancy is the mean number of years of life remaining at a given age, assuming constant mortality rates. It is denoted by ,[a] which means the average number of subsequent years of life for someone now aged , according to a particular mortality experience. Longevity and life expectancy are not synonyms. Life expectancy is defined statistically as the average number of years remaining for an individual or a group of people at a given age. Longevity refers to the characteristics of the relatively long life span of some members of a population. Moreover, because life expectancy is an average, a particular person may well die many years before or many years after their "expected" survival. The term "maximum life span" has a quite different meaning and is more related to longevity.
Life expectancy is also used in plant or animal ecology; life tables (also known as actuarial tables). The term life expectancy may also be used in the context of manufactured objects, although the related term shelf life is used for consumer products and the terms "mean time to breakdown" (MTTB) and "mean time between failures" (MTBF) are used in engineering.
Human life expectancy patterns
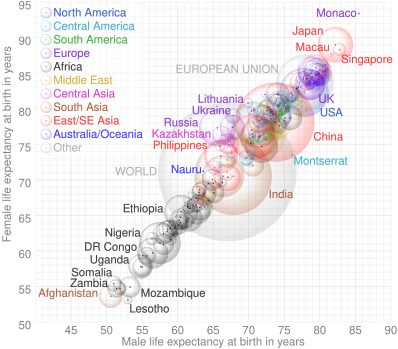
Human beings are expected to live on average 49.42 years in Swaziland and 82.6 years in Japan, although Japan's recorded life expectancy may have been very slightly increased by counting many infant deaths as stillborn. An analysis published in 2011 in The Lancet attributes Japanese life expectancy to equal opportunities and public health as well as diet.
The oldest confirmed recorded age for any human is 122 years (see Jeanne Calment). This is referred to as the "maximum life span", which is the upper boundary of life, the maximum number of years any human is known to have lived.
Life expectancy variation over time
The following information is derived from Encyclopædia Britannica, 1961 and other sources, some with a questionable accuracy. Unless otherwise stated, it represents estimates of the life expectancies of the world population as a whole. In many instances, life expectancy varied considerably according to class and gender.
Life expectancy at birth takes account of infant mortality, but not pre-natal mortality.
Life expectancy increases with age as the individual survives the higher mortality rates associated with childhood. For instance, the table above listed the life expectancy at birth among 13th-century English nobles at 30. Having survived until the age of 21, a male member of the English aristocracy in this period could expect to live:
- 1200â€"1300: to age 64
- 1300â€"1400: to age 45 (due to the impact of the bubonic plague)
- 1400â€"1500: to age 69
- 1500â€"1550: to age 71
In general, the available data indicate that longer lifespans became more common recently in human evolution. This increased longevity is attributed by some writers to cultural adaptations rather than genetic evolution, although some research indicates that during the Neolithic Revolution natural selection favored increased longevity. Nevertheless, all researchers acknowledge the effect of cultural adaptations upon life expectancy.
17th-century English life expectancy was only about 35 years, largely because infant and child mortality remained high. life expectancy was under 25 years in the early Colony of Virginia, and in seventeenth-century New England, about 40 per cent died before reaching adulthood. During the Industrial Revolution, the life expectancy of children increased dramatically. The under-5 mortality rate in London decreased from 745 in 1730â€"1749 to 318 in 1810â€"1829.
Public health measures are credited with much of the recent increase in life expectancy. During the 20th century, despite a brief drop due to the 1918 flu pandemic starting around that time the average lifespan in the United States increased by more than 30 years, of which 25 years can be attributed to advances in public health.
Regional variations
There are great variations in life expectancy between different parts of the world, mostly caused by differences in public health, medical care, and diet. The impact of AIDS on life expectancy is particularly notable in many African countries. According to projections made by the United Nations (UN) in 2002, the life expectancy at birth for 2010â€"2015 (if HIV/AIDS did not exist) would have been:
- 70.7 years instead of 31.6 in Botswana
- 69.9 years instead of 41.5 in South Africa
- 70.5 years instead of 31.8 in Zimbabwe
The UN's predictions were too pessimistic. Actual life expectancy in Botswana declined from 65 in 1990 to 49 in 2000 before increasing to 66 in 2011. In South Africa, life expectancy was 63 in 1990, 57 in 2000, and 58 in 2011. And in Zimbabwe, life expectancy was 60 in 1990, 43 in 2000, and 54 in 2011.
During the last 200 years, African countries have generally not had the same improvements in mortality rates that have been enjoyed by countries in Asia, Latin America, and Europe.
In the United States, African-American people have shorter life expectancies than their European-American counterparts. For example, white Americans born in 2010 are expected to live until age 78.9, but black Americans only until age 75.1. This 3.8-year gap, however, is the lowest it has been since at least 1975. The greatest difference was 7.1 years in 1993. In contrast, Asian-American women live the longest of all ethnic groups in the United States, with a life expectancy of 85.8 years. The life expectancy of Hispanic Americans is 81.2 years.
Cities also experience a wide range of life expectancy based on neighborhood breakdowns. This is largely due to economic clustering and poverty conditions that tend to associate based on geographic location. Multi-generational poverty found in struggling neighborhoods also contributes. In United States cities such as Cincinnati, the life expectancy gap between low income and high income neighborhoods touches 20 years.
Economic circumstances
Economic circumstances also affect life expectancy. For example, in the United Kingdom, life expectancy in the wealthiest areas is several years longer than in the poorest areas. This may reflect factors such as diet and lifestyle, as well as access to medical care. It may also reflect a selective effect: people with chronic life-threatening illnesses are less likely to become wealthy or to reside in affluent areas. In Glasgow, the disparity is amongst the highest in the world: life expectancy for males in the heavily deprived Calton area stands at 54, which is 28 years less than in the affluent area of Lenzie, which is only 8Â km away.
A 2013 study found a pronounced relationship between economic inequality and life expectancy. However, a study by José A. Tapia Granados and Ana Diez Roux at the University of Michigan found that life expectancy actually increased during the Great Depression, and during recessions and depressions in general. The authors suggest that when people are working extra hard during good economic times, they undergo more stress, exposure to pollution, and likelihood of injury among other longevity-limiting factors.
Life expectancy is also likely to be affected by exposure to high levels of highway air pollution or industrial air pollution. This is one way that occupation can have a major effect on life expectancy. Coal miners (and in prior generations, asbestos cutters) often have shorter than average life expectancies. Other factors affecting an individual's life expectancy are genetic disorders, drug use, tobacco smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, access to health care, diet and exercise.
Gender differences
Women tend to have a lower mortality rate at every age. In the womb, male fetuses have a higher mortality rate (babies are conceived in a ratio estimated to be from 107 to 170 males to 100 females, but the ratio at birth in the United States is only 105 males to 100 females). Among the smallest premature babies (those under 2 pounds or 900 g), females again have a higher survival rate. At the other extreme, about 90% of individuals aged 110 are female. The difference in life expectancy between men and women in the United States dropped from 7.8 years in 1979 to 5.3 years in 2005, with women expected to live to age 80.1 in 2005. Also, data from the UK shows the gap in life expectancy between men and women decreasing in later life. This may be attributable to the effects of infant mortality and young adult death rates.
In the past, mortality rates for females in child-bearing age groups were higher than for males at the same age. This is no longer the case, and female human life expectancy is considerably higher than that of males. The reasons for this are not entirely certain. Traditional arguments tend to favor socio-environmental factors: historically, men have generally consumed more tobacco, alcohol and drugs than women in most societies, and are more likely to die from many associated diseases such as lung cancer, tuberculosis and cirrhosis of the liver. Men are also more likely to die from injuries, whether unintentional (such as occupational war or car accidents) or intentional (suicide). Men are also more likely to die from most of the leading causes of death (some already stated above) than women. Some of these in the United States include: cancer of the respiratory system, motor vehicle accidents, suicide, cirrhosis of the liver, emphysema, prostate cancer, and coronary heart disease. These far outweigh the female mortality rate from breast cancer and cervical cancer.
Some argue that shorter male life expectancy is merely another manifestation of the general rule, seen in all mammal species, that larger (size) individuals (within a species) tend, on average, to have shorter lives. This biological difference occurs because women have more resistance to infections and degenerative diseases.
In her extensive review of the existing literature, Kalben concluded that the fact that women live longer than men was observed at least as far back as 1750 and that, with relatively equal treatment, today males in all parts of the world experience greater mortality than females. Of 72 selected causes of death, only 6 yielded greater female than male age-adjusted death rates in 1998 in the United States. With the exception of birds, for almost all of the animal species studied, males have higher mortality than females. Evidence suggests that the sex mortality differential in people is due to both biological/genetic and environmental/behavioral risk and protective factors.
There is a recent suggestion that mitochondrial mutations that shorten lifespan continue to be expressed in males (but less so in females) because mitochondria are inherited only through the mother. By contrast, natural selection weeds out mitochondria that reduce female survival; therefore such mitochondria are less likely to be passed on to the next generation. This thus suggests that females tend to live longer than males. The authors claim that this is a partial explanation.
In developed countries, starting around 1880, death rates decreased faster among women, leading to differences in mortality rates between males and females. Before 1880 death rates were the same. In people born after 1900, the death rate of 50- to 70-year-old men was double that of women of the same age. Cardiovascular disease was the main cause of the higher death rates among men. Men may be more vulnerable to cardiovascular disease than women, but this susceptibility was evident only after deaths from other causes, such as infections, started to decline.
Centenarians
In developed countries, the number of centenarians is increasing at approximately 5.5% per year, which means doubling the centenarian population every 13 years, pushing it from some 455,000 in 2009 to 4.1 million in 2050. Japan is the country with the highest ratio of centenarians (347 for every 1 million inhabitants in September 2010). Shimane prefecture had an estimated 743 centenarians per million inhabitants.
In the United States, the number of centenarians grew from 32,194 in 1980 to 71,944 in November 2010 (232 centenarians per million inhabitants).
Mental Illness
The seriously mentally ill have a 10 to 25 year reduction in life expectancy. This reduction in life is mostly due to preventable diseases.
Evolution and aging rate

Various species of plants and animals, including humans, have different lifespans. Evolutionary theory states that organisms that, by virtue of their defenses or lifestyle, live for long periods whilst avoiding accidents, disease, predation, etc., are likely to have genes that code for slow aging â€" which often translates to good cellular repair. This is theorized to be true because if predation or accidental deaths prevent most individuals from living to an old age, then there will be less natural selection to increase intrinsic life span. The finding was supported in a classic study of opossums by Austad, however, the opposite relationship was found in an equally prominent study of guppies by Reznick.
One prominent and very popular theory states that lifespan can be lengthened by a tight budget for food energy called caloric restriction. Caloric restriction observed in many animals (most notably mice and rats), shows a near doubling of life span due to a very limited calorific intake. Support for this theory has been bolstered by several new studies linking lower basal metabolic rate to increased life expectancy. This is the key to why animals like giant tortoises can live so long. Studies of humans with 100+ year life spans have shown a link to decreased thyroid activity, resulting in their lowered metabolic rate.
In a broad survey of zoo animals, no relationship was found between the fertility of the animal and its life span.
Calculating life expectancy

The starting point for calculating life expectancy is the age-specific death rates of the population members. If a large amount of data is available, the age-specific death rates can be simply taken as the mortality rates actually experienced at each age (i.e. the number of deaths divided by the number of years "exposed to risk" in each data cell). However it is customary to apply smoothing to iron out as far as possible the random statistical fluctuations from one year of age to the next. In the past, a very simple model used for this purpose was the Gompertz function, although these days more sophisticated methods are used.
The most common methods used for this purpose nowadays are:
- to fit a mathematical formula, such as an extension of the Gompertz function, to the data,
- for relatively small amounts of data, to look at an established mortality table previously derived for a larger population and make a simple adjustment to it (e.g. multiply by a constant factor) to fit the data.
- with a large amount of data, one looks at the mortality rates actually experienced at each age, and applies smoothing (e.g. by cubic splines).
While the data required are easily identified in the case of humans, the computation of life expectancy of industrial products and wild animals involves more indirect techniques. The life expectancy and demography of wild animals are often estimated by capturing, marking and recapturing them. The life of a product, more often termed shelf life, is also computed using similar methods. In the case of long-lived components, such as those used in critical applications, e.g. in aircraft, methods like accelerated aging are used to model the life expectancy of a component.
The age-specific death rates are calculated separately for separate groups of data that are believed to have different mortality rates (e.g. males and females, and perhaps smokers and non-smokers if data is available separately for those groups) and are then used to calculate a life table, from which one can calculate the probability of surviving to each age. In actuarial notation, the probability of surviving from age to age is denoted and the probability of dying during age (i.e. between ages and ) is denoted . For example, if 10% of a group of people alive at their 90th birthday die before their 91st birthday, then the age-specific death probability at age 90 would be 10%. Note that this is a probability rather than a mortality rate.
The expected future lifetime of a life age in whole years (the curtate expected lifetime of (x)) is denoted by the symbol .[a] It is the conditional expected future lifetime (in whole years), assuming survival to age . If denotes the curtate future lifetime at , then : Substituting in the sum and simplifying, we get the equivalent formula: If we make the assumption that, on average, people live a half year in the year of death, then the complete expectation of future lifetime at age is .
Life expectancy is by definition an arithmetic mean. It can also be calculated by integrating the survival curve from ages 0 to positive infinity (or equivalently to the maximum lifespan, sometimes called 'omega'). For an extinct or completed cohort (all people born in year 1850, for example), of course, it can simply be calculated by averaging the ages at death. For cohorts with some survivors, it is estimated by using mortality experience in recent years. These estimates are called period cohort life expectancies.
It is important to note that this statistic is usually based on past mortality experience, and assumes that the same age-specific mortality rates will continue into the future. Thus such life expectancy figures need to be adjusted for temporal trends before calculating how long a currently living individual of a particular age is expected to live. Period life expectancy remains a commonly used statistic to summarize the current health status of a population.
However, for some purposes, such as pensions calculations, it is usual to adjust the life table used, thus assuming that age-specific death rates will continue to decrease over the years, as they have usually done in the past. This is often done by simply extrapolating past trends; however, some models do exist to account for the evolution of mortality (e.g. the Leeâ€"Carter model).
As discussed above, on an individual basis, there are a number of factors that have been shown to correlate with a longer life. Factors that are associated with variations in life expectancy include family history, marital status, economic status, physique, exercise, diet, drug use including smoking and alcohol consumption, disposition, education, environment, sleep, climate, and health care.
Healthy life expectancy
In order to assess the quality of these additional years of life, 'healthy life expectancies' have been calculated for the last 30 years. Since 2001, the World Health Organization has published statistics called Healthy life expectancy (HALE), defined as the average number of years that a person can expect to live in "full health", excluding the years lived in less than full health due to disease and/or injury. Since 2004, Eurostat publishes annual statistics called Healthy Life Years (HLY) based on reported activity limitations. The United States of America uses similar indicators in the framework of their nationwide health promotion and disease prevention plan "Healthy People 2010". An increasing number of countries are using health expectancy indicators to monitor the health of their population.
Life expectancy forecasting
Forecasting life expectancy and mortality forms an important subdivision of demography. Future trends in life expectancy have huge implications for old-age support programs like U.S. Social Security and pension systems, because the cash flow in these systems depends on the number of recipients still living (along with the rate of return on the investments or the tax rate in PAYGO systems). With longer life expectancies, these systems see increased cash outflow; if these systems underestimate increases in life-expectancies, they won't be prepared for the large payments that will inevitably occur as humans live longer and longer.
Life expectancy forecasting usually is based on two different approaches:
- Forecasting the life expectancy directly, generally using ARIMA or other time series extrapolation procedures: This approach has the advantage of simplicity, but it cannot account for changes in mortality at specific ages, and the forecasted number cannot be used to derive other life table results. Analyses and forecasts using this approach can be done with any common statistical/ mathematical software package, like EViews, R, SAS, Stata, Matlab, or SPSS.
- Forecasting age specific death rates and computing the life expectancy from the results with life table methods: This approach is usually more complex than simply forecasting life expectancy because the analyst must deal with correlated age specific mortality rates, but it seems to be more robust than simple one-dimensional time series approaches. This approach also yields a set of age specific rates that may be used to derive other measures, like survival curves or life expectancies at different ages. The most important approach within this group is the Lee-Carter model, which uses the singular value decomposition on a set of transformed age-specific mortality rates to reduce their dimensionality to a single time series, forecasts that time series, and then recovers a full set of age-specific mortality rates from that forecasted value. Software for this approach include Professor Rob J. Hyndman's R package called `demography` and UC Berkeley's LCFIT system.
Policy uses of life expectancy
Life expectancy is one of the factors in measuring the Human Development Index (HDI) of each nation, along with adult literacy, education, and standard of living.
Life expectancy is also used in describing the physical quality of life of an area or, for an individual, when determining the value of a life settlement, a life insurance policy sold for a cash asset.
Disparities in life expectancy are often cited as demonstrating the need for better medical care or increased social support. A strongly associated indirect measure is income inequality. For the top 21 industrialised countries, counting each person equally, life expectancy is lower in more unequal countries (r = -.907). There is a similar relationship among states in the US (r = -.620).
Life expectancy vs. life span
Life expectancy differs from maximum life span. Life expectancy is an average, computed over all people including those who die shortly after birth, those who die in early adulthood in childbirth or in wars, and those who live unimpeded until old age, whereas lifespan is an individual-specific concept and maximum lifespan is an upper bound rather than an average.
It can be argued that it is better to compare life expectancies of the period after childhood to get a better handle on life span. Life expectancy can change dramatically after childhood, as is demonstrated by the Roman Life Expectancy table where at birth the life expectancy was 21 but by the age of 5 it jumped to 42. Studies like Plymouth Plantation; "Dead at Forty" and Life Expectancy by Age, 1850â€"2004 similarly show a dramatic increase in life expectancy once adulthood was reached.
See also
Increasing life expectancy
Notes
a. ^ ^ In standard actuarial notation, ex refers to the expected future lifetime of (x) in whole years, while ex with a circle above the e denotes the complete expected future lifetime of (x), including the fraction.
References
Further reading
- Leonid A. Gavrilov & Natalia S. Gavrilova (1991), The Biology of Life Span: A Quantitative Approach. New York: Harwood Academic Publisher, ISBN 3-7186-4983-7
- Kochanek, Kenneth D., Elizabeth Arias, and Robert N. Anderson (2013), How Did Cause of Death Contribute to Racial Differences in Life Expectancy in the United States in 2010?. Hyattsville, Md.: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics.
External links
- Charts for all countries
- Global Agewatch has the latest internationally comparable statistics on life expectancy from 195 countries.
- Rank Order - Life expectancy at birth from the CIA's World Factbook.
- CDC year-by-year life expectancy figures for USA from the USA Centers for Disease Controls and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics.
- Life expectancy in Roman times from the University of Texas.
- Animal lifespans: Animal Lifespans from Tesarta Online (Internet Archive); The Life Span of Animals from Dr Bob's All Creatures Site.
