Cathine, also known as d-norpseudoephedrine, is a psychoactive drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes which acts as a stimulant. Along with cathinone, it is found naturally in Catha edulis (khat), and contributes to its overall effects. It has approximately 10-14% the potency of amphetamine.
Pharmacology
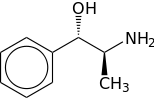
Like amphetamines, cathinone, and ephedrine, cathine acts as a releasing agent of norepinephrine and epinephrine, or as a norepinephrine releasing agent (NRA). It also acts as a dopamine releasing agent (DRA) to a lesser extent.
Chemistry

Cathine is one of the optical isomers of phenylpropanolamine (PPA).
Regulation

The World Anti-Doping Agency's list of prohibited substances (used for the Olympic Games among other athletic events) bars cathine in concentrations of over 5 micrograms per milliliter in urine. Cathine is a Schedule III drug under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances. In the United States, it is classified as a Schedule IV controlled substance.
In Hong Kong, cathine is regulated under Schedule 1 of Hong Kong's Chapter 134 Dangerous Drugs Ordinance. Unlawful possession is punishable by severe fines and imprisonment.
See also
- L-Norpseudoephedrine, an enantiomer
- Phenylpropanolamine
- Catha Edulis ("Khat")
- Cathinone
- Methcathinone
- Ephedra Sinica ("Ephedra")
- Ephedrine
- Pseudoephedrine
- Phenethylamine
- Amphetamine
- Methamphetamine
